Cyber security courses: your pathway to an in-demand field
Growing demand for cyber security professionals
Roles that tackle cyber crime are in high-demand – increasingly becoming key to nearly every industry in the world. Constantly changing technology creates new opportunities for cyber criminals to attack individuals and businesses.
Despite recent efforts to boost the number of professionals working in the cyber security industry, demand for skilled graduates remains high, and the salaries reflect that: cyber security analysts receive a salary of between $100,000 and $120,000 on average.
Start your journey now – explore cyber security courses at VU to unlock a high-paying, high-demand career.
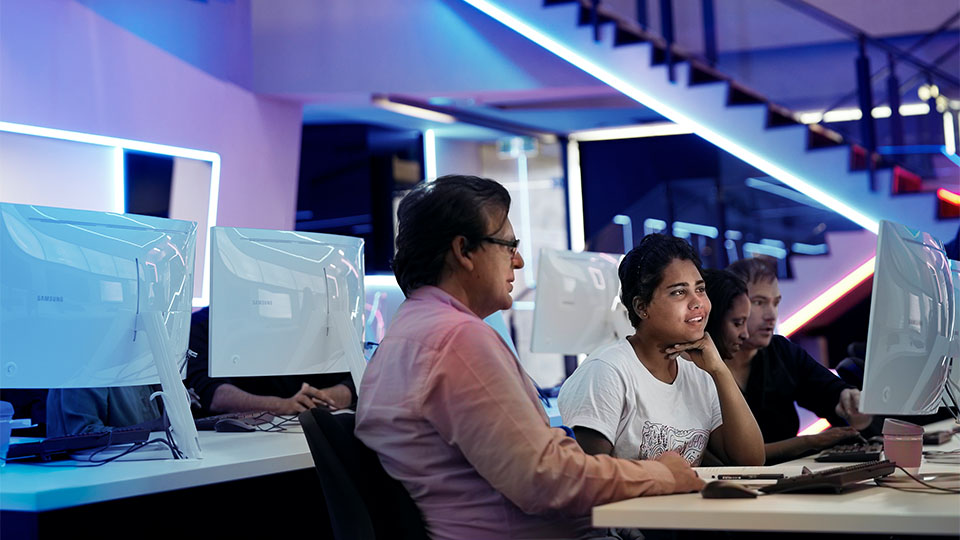

What cyber security jobs can I get after studying?
The Australian Government’s 2024 Skills Priority List reveals a notable shortage of cyber security professionals in every Australian state and territory, including:
- cyber security advice and assessment specialists
- cyber security analysts
- cyber security architects
- cyber engineers (except NT)
- cyber security operations coordinators.
With so much of our work and lives playing out online today, cyber crime can impact just about every person and organisation in Australia. This means there’s a huge need to fill cyber security jobs across just about every industry, from finance and retail to education, government, healthcare and critical infrastructure.
According to a 2024 report from industry body Austcyber, we’ll need an extra 5000 workers every year in Australia to avoid hitting a shortfall in 2030.
Industry intel

Cyber attacks on the rise in Australia
In 2024, we saw the highest number of data breaches affecting businesses in the previous three and a half years. Phishing and web application attacks accounted for most reported breaches.
Two high-profile data breaches in 2022 affecting Optus and Medibank put a spotlight on the growing issue. The latter incident saw more than one in three Australians potentially having their personal information publicly leaked.
Key insights from the 2023-24 Annual Cyber Threat Report
Every year, the Australian Signals Directorate (ASD) releases a report detailing the latest cyber threats affecting organisations, businesses, critical infrastructure and individuals. The latest findings highlight the continued exploitation of Australian networks and the evolving nature of the attacks.



Artificial intelligence presents cyber security risks & opportunities
Cyber criminals continue to use AI or machine learning (ML) to accelerate, automate or enhance various attacks. This can range from scams that employ deepfake audio or video to algorithms that identify vulnerabilities, interfere with system operations and adapt to avoid detection.
On the other hand, AI can also enhance cyber security protocols. This includes automating routine tasks like detecting potential threats, encrypting data and checking for new patches and software updates.

Diverse career paths in cyber security
With a career in cyber security, you can find the path that best suits you. From ethical hacking to security consulting, there are different cyber security jobs to choose from based on your interests and skill sets.
What do cyber security analysts do?
As a cyber security analyst, you’ll monitor, prevent and stop cyber attacks. You’ll use your deep understanding of malware and cyber crime to implement and maintain security features. Most of your work is preventative, with tasks that include assessing potential vulnerabilities, monitoring the dark web for sensitive data, advising on cyber security measures, documenting any attempted cyber attacks and restoring protection after breaches by identifying the source and gateway for the attack.
What do cyber security advice & assessment specialists do?
Cyber security advice and assessment specialists focus on managing risk, often through security control assessments. Working either as an external advisor or within an organisation, your tasks can include reviewing security policy, developing standards and guidelines, developing security strategies and system designs and providing advice on threats and vulnerabilities.
What do cyber security architects do?
Design, develop and implement systems to support an organisation's IT network as a highly specialised cyber security architect. Using the latest technologies and methods, you’ll create a comprehensive security architecture designed to protect sensitive data while working behind the scenes to actively monitor threats and prevent breaches.
What do cyber engineers do?
As a cyber engineer, or cyber security engineer, you’ll design, implement and maintain security systems to protect an organisation's computer networks, systems, and data from cyber threats. This includes identifying vulnerabilities, monitoring network activity, creating security architectures, deploying security tools and responding to any incidents.
What do cyber security operations coordinators do?
Cyber security operations coordinators oversee planning for and responding to complex cyber security incidents. Your role includes incident response management, actively hunting for hidden threats and potential malicious activity, technical analysis, capacity building and policy and procedure development.
What do ethical hackers do?
Ethical hackers test an organisation’s cyber security defences to help address any vulnerabilities. You’ll simulate cyber attacks (penetration testing) to detect weaknesses and help improve the security of networks, systems, applications and software. The type of simulated attacks can range from trying to breach firewalls to social engineering attempts like simulated phishing emails.
What do governance, risk and compliance (GRC) specialists do?
As a GRC specialist, you’ll focus on ensuring organisations comply with relevant Australian regulations and industry standards. This includes implementing cyber security strategies according to the ASD Essential Eight principles*, managing risks effectively and maintaining robust cyber security policies and procedures.
Non-technical cyber security roles
In addition to GRC specialists, other non-technical jobs you can get into after studying cyber security include cyber sales, security awareness, account management, project management and education. These roles also pay well and suit those who have stronger soft skills and are interested in the cyber security industry.
*What is the Essential Eight?
The ASD created the Essential Eight as a series of baseline strategies to help organisations prevent and minimise cyber security incidents. These include:
- Application control – Add appropriate controls and approvals on user applications
- Application patching – Keep third-party applications up-to-date
- Operating system patching – Keep operating systems up-to-date
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) – Enforce MFA for all web and third-party services
- Microsoft Office macro settings – Limiting access to run macros in MO
- User application hardening – Placing basic limits on user applications
- Restrict administrative privileges – Manage access to applications and operating systems based on specific user duties.
- Daily backup and recovery strategy – Commence regular offline backups and test recovery process.
Learn more: Essential Eight Explained
How much can you earn as a cyber security professional?
Want to know how much money you could make in different cyber security jobs? Here’s a breakdown of average salaries for some of the key, in-demand roles across Australia.
| Role | Average cyber security salary in Australia |
|---|---|
| Cyber security analyst | $115,000 |
| Cyber security advice and assessment specialist | $120,000 |
| Cyber security architect | $185,000 |
| Cyber engineer | $150,000 |
| Governance, risk and compliance (GRC) specialist | $140,000 |
[source: Seek data, 2025]
How to become a cyber security professional
Looking to enter the cyber security field? Here at VU, we have the courses, facilities and industry partnerships to help you succeed. Discover your unique career journey with multiple cyber security study pathways available based on where you are in life.
Certificate IV in Cyber Security (22603VIC)
Kickstart your career sooner with a cyber security TAFE course. The Certificate IV in Cyber Security (22603VIC) equips you with current best-practice skills, getting you qualified to work as a cyber security technician in IT support across businesses, organisations and government. Over this one-year full time course, you’ll learn in-demand skills so you're job-ready as soon as you graduate, including how to:
- monitor cyber security risks
- prevent attacks using software, tools, policy and procedure
- minimise the risk of insider security breaches
- reduce network vulnerabilities by developing systems.
As a VU student, you’ll get to access paid and volunteer placements supporting the IT and cyber security needs of local small businesses. Eligible students can also study for free* if you first complete the ICT30120 Certificate III in Information Technology. After completing the Certificate IV at VU, you’re guaranteed a place in our Bachelor of Cyber Security course.
*Student services and materials fees still apply.
Diploma of Cyber Security
Learn how to protect organisations against evolving cyber security threats in the Diploma of Cyber Security. Whether you're considering a career change or are a recent graduate from another course, this qualification is your gateway to secure a job in an industry desperate for more workers. In this one year undergraduate course, you’ll build foundational knowledge and in-demand skills needed to combat the latest threats, including:
- conducting threat analysis and vulnerability assessments
- overseeing cyber security incident responses
- managing and strengthening network security
- uncovering threats and addressing vulnerabilities through digital forensics and ethical hacking.
After graduating, you'll be prepared to enter the workforce with confidence, having gained hands-on experience in our state-of-the-art facilities with guidance from industry experts.
Once you complete this diploma, you’re guaranteed a place in the second year of the Bachelor of Cyber Security at VU.
Bachelor of Cyber Security
Launch your career journey as a cyber security professional with a Bachelor of Cyber Security. Gain comprehensive knowledge and skills around protecting data and IT systems from cyber crime, developing your expertise across multiple disciplines, from how information technology works to specialised cyber security skills such as:
- vulnerability analysis and control
- understanding and implementing cyber security regulation, policies and laws
- developing software
- designing networks
- developing and implementing firewalls, digital signatures, virtual private networks, firewalls, intrusion detection, data encryption and other cyber security technologies.
Benefit from our strong partnerships with industry leaders like Microsoft, Oracle and AWS. Graduate with an internationally recognised degree so you can work in Australia or take your career overseas.
Graduate Certificate in Cyber Security
Build your cyber security expertise in the six month (full time) Graduate Certificate in Cyber Security. This postgraduate IT course takes you through the essentials of cyber security, including:
- detecting cyber security threats
- managing cyber security architecture
- cloud security best practice
- managing enterprise security
- cyber security policies, laws and regulations
- using public key infrastructure, digital signatures, virtual private networks, firewalls, data encryption and intrusion detection technologies.
Learn how to apply the latest cyber security strategies in ever-evolving situations from experienced researchers and industry experts. Once you graduate, you’ll access new career opportunities in the fast-growing cyber security industry.
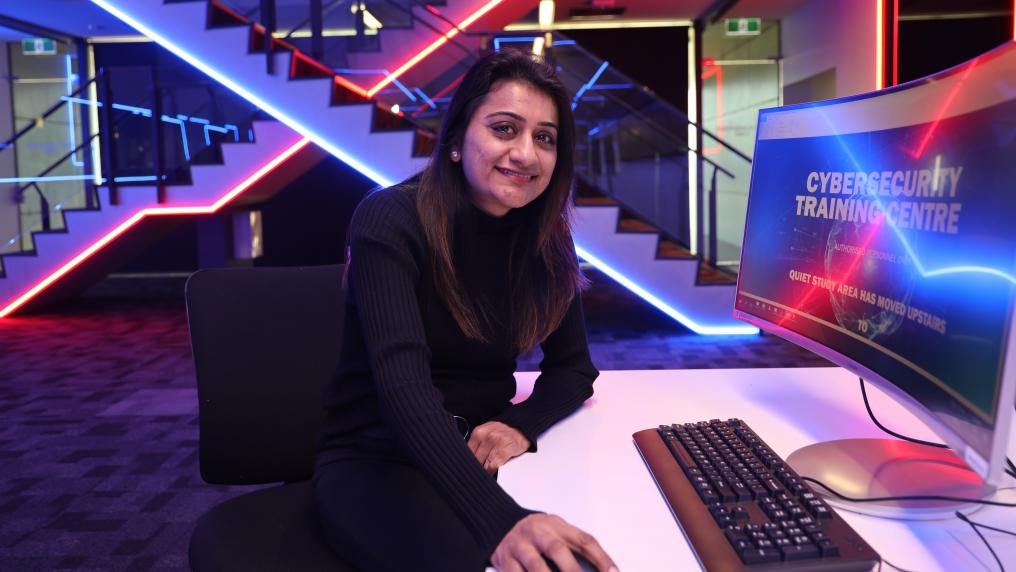
Build real-world skills at VU’s Cyber Security Training Centre
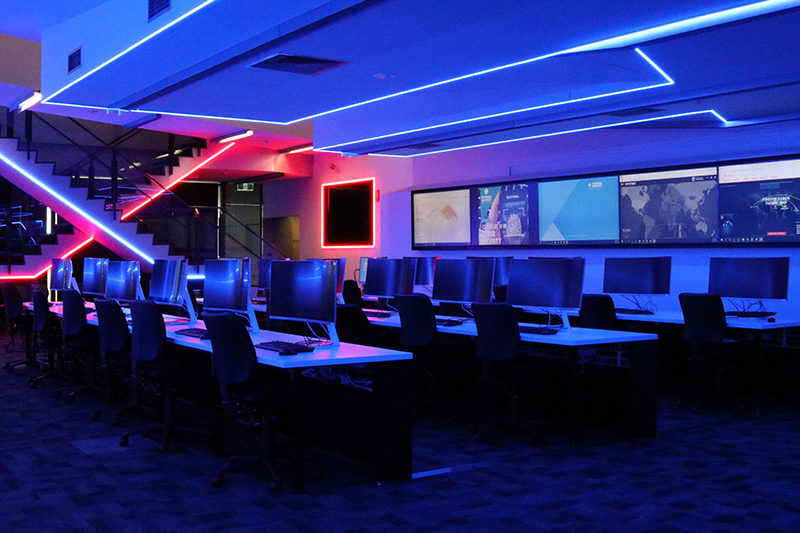

Get hands-on training at VU’s Cyber Security Training Centre at our St Albans Campus. Designed to provide you with real-life training scenarios, you’ll build your skills and knowledge in the simulated Security Operations Centre (SOC). This includes an active working environment with red 'attack' and blue 'defend' rooms, where you get a chance to take on real-time roles as either data hackers or cyber security protectors. You’ll develop work-ready skills with confidence while participating in engaging, practical learning activities.
Part of our strategy to address the short fall in Australian cyber security professionals is by providing up-to-date training and skills development in purpose-built facilities. Our Cyber Security Training Centre is the result of a partnership between industry and education, encouraging more students to develop skills critical to a range of industries – from retail to finance, law, healthcare, education and government.
Cyber security courses co-designed by industry professionals
VU’s cyber security courses are designed in consultation with leading cyber security professionals. This ensures we deliver learning experiences that are relevant to industry today. Combined with real-world training exercises in our Cyber Security Training Centre, you’ll graduate with the expertise you need to start your career in the industry immediately.
How to get into cyber security: discover the right pathway for you
With TAFE courses, Higher Education courses and pathways in between, we’ve got study pathways to suit every person interested in pursuing a career in cyber security. Just finished Year 12? Jump straight into the Bachelor of Cyber Security. At VU, you don’t need an ATAR to get into this course.
Those who complete the following courses are also guaranteed a place in the Bachelor of Cyber Security, often with credits going towards their degree:
- Certificate IV in Cyber Security (22603VIC) (24 credit points)
- Certificate IV in Information Technology (ICT40120) (24 credit points)
- Diploma of Information Technology (96 credit points)
- International Foundations at VU (no credit, guaranteed entry only)
At VU, you’ll get the knowledge, skills and practical experience you need to successfully launch your career and enjoy a rewarding profession protecting our digital landscape.
Cyber security safety is a shared responsibility
The findings of the 23-24 Annual Cyber Threat Report highlight the critical importance of robust cyber security measures. Comprehensive and carefully designed cyber security strategies, along with industry professionals to implement them, are key to combating increasingly sophisticated and rapidly growing cyber crime.
Individuals, organisations, businesses, governments, researchers and education institutions must all continue to collaborate to leverage the latest insights and determine the best way to address evolving cyber threats. As a fresh cyber security graduate, you can use your new skills and expertise to help build a safer digital environment for everyone.
Help fight growing cyber crime: explore cyber security courses at VU
Whether you’re just starting out or you’re an IT professional looking to advance in the field, the world of cyber security offers a promising future for your career. Apply for a course at VU and get the skills to tackle cyber crime.
- Develop skills in our world-class Cyber Security Training Centre.
- Learn through gamified challenges designed by global experts.
- Get immersed in industry with opportunities through partners like Microsoft and Oracle.
- Choose to study online for select courses, or a combination of online and in-person.
- Upskill with Free TAFE* or choose from courses across all levels of study.
Explore cyber security courses at VU
*Free TAFE is available to eligible students only. Free TAFE courses are free of tuition fees, but student services and materials fees still apply.
Cyber security at VU: an insider look
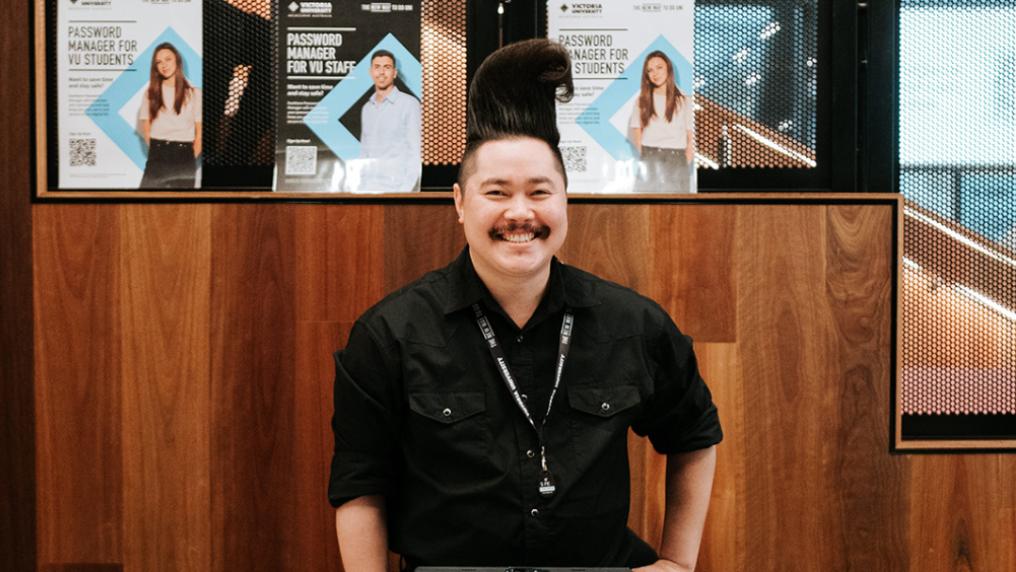
Ez Yiap is VU’s cyber influence lead. He’s focused on promoting cyber security awareness and culture among staff, students, partners, suppliers, service providers and VU’s wider community.
Ez is the face of all things cyber at VU – you’ll see him popping up everywhere from O-fest to Open Day to promote being safe, savvy and secure online.
VU maintains a holistic cyber security program, focusing on defence in-depth and layered security controls aligned to the NIST Cyber Security Framework (CSF). Our team includes cyber security analysts, cyber security engineers, security awareness and training managers, identity and access managers, cyber risk managers and a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO).



